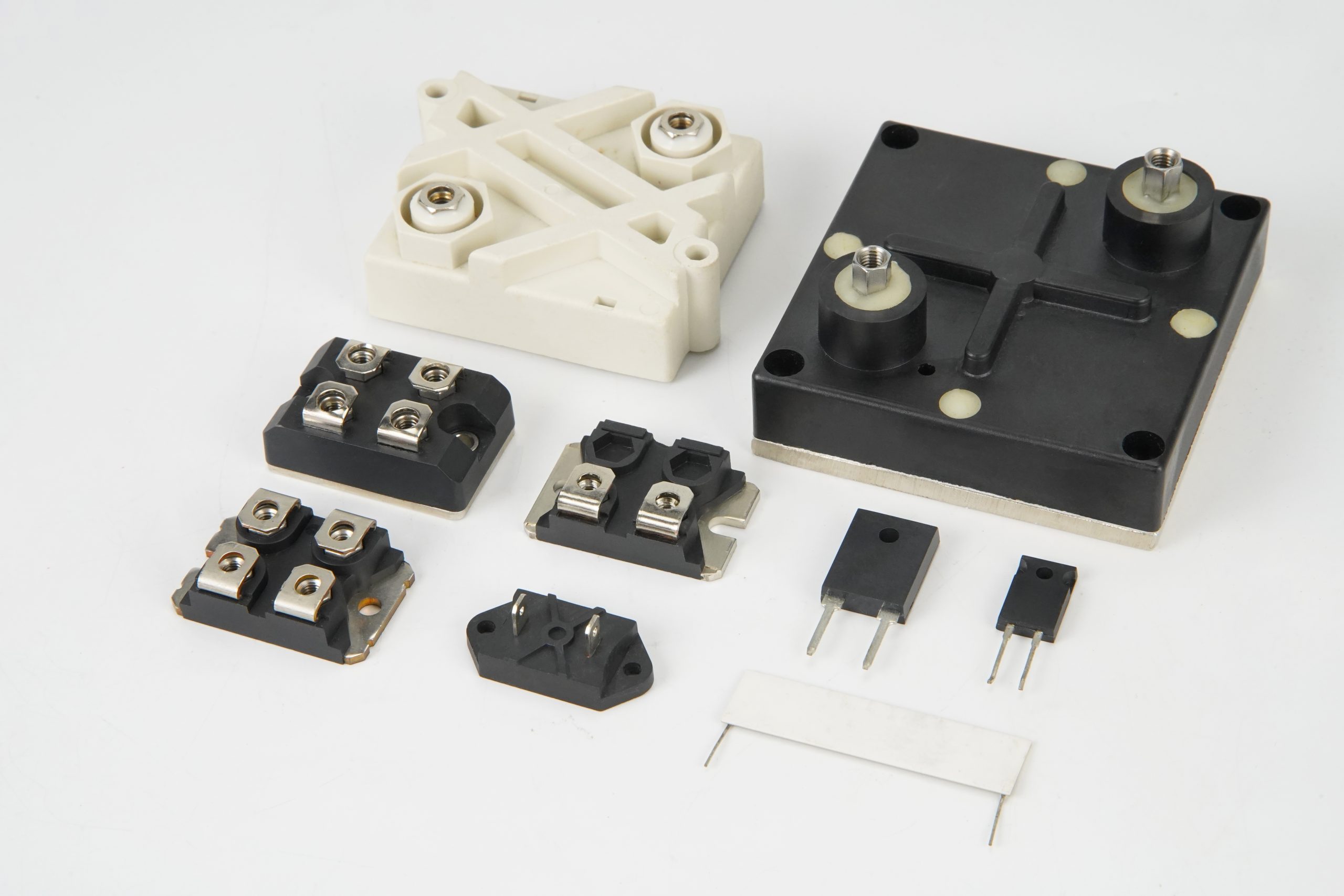
In the fast-evolving world of power electronics, the thick film power resistor stands out as a robust and versatile component essential for demanding applications. These resistors, constructed from a thick layer of resistive material screen-printed onto a ceramic substrate, offer unparalleled performance in handling high power levels while maintaining precision and reliability. Whether you’re designing power supplies, industrial controls, or automotive systems, a thick film power resistor ensures efficient energy management and protection against surges. With power ratings from 250W to 2000W, they are engineered for scenarios where traditional resistors fall short, providing low inductance and high voltage isolation that make them indispensable in modern circuitry.
As industries push toward higher efficiency and compactness, the demand for advanced thick film power resistors has surged. These devices not only dissipate heat effectively but also deliver stable resistance values across extreme conditions, making them a go-to choice for engineers seeking durability without compromising on size or cost. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore the key specifications, advantages, and primary applications of thick film power resistors, highlighting why they are the backbone of reliable power systems.
Understanding Thick Film Power Resistors: Construction and Working Principle
At its core, a thick film power resistor is built by depositing a conductive paste—typically containing metal oxides like ruthenium or tantalum—onto an insulating ceramic base such as aluminum oxide. This paste is then sintered at high temperatures to form a durable resistive film that’s significantly thicker than its thin-film counterparts, allowing for superior heat dissipation through convection and radiation. Unlike wirewound resistors, which can introduce unwanted inductance, thick film power resistors are inherently non-inductive, making them ideal for high-frequency operations.
The working mechanism revolves around controlled current flow through the resistive layer, where excess energy is converted to heat and safely dissipated. This design enables thick film power resistors to handle pulse loads and surges without hotspots, thanks to the even distribution of heat across the film’s surface. For power-intensive setups, they can be mounted on heatsinks or cold plates, boosting dissipation capacity up to 2kW in compact 60mm square formats. This construction not only enhances mechanical robustness but also ensures compliance with standards like RoHS and AEC-Q200, proving their reliability in harsh environments.
Key Specifications of High-Quality Thick Film Power Resistors
When selecting a thick film power resistor, specifications are paramount to match your application’s needs.
Our premium models boast:
- Power Rating: 250W to 2000W, supporting everything from moderate industrial loads to heavy-duty power conversion.
- Resistance Range: A versatile 0.1Ω to 100MΩ, allowing precise tuning for diverse circuit requirements, with tolerances as tight as ±0.05% to ±30%.
- Parasitic Inductance: Less than 40nH, minimizing signal distortion in high-speed circuits like PWM filters.
- Insulation Withstand Voltage: Up to 12kVrms, ensuring safety in high-voltage isolation scenarios.
- Partial Discharge: Rated at 8kVrms with less than 10pc, preventing arcing and extending component lifespan.
These specs, combined with a temperature coefficient of ±100ppm/°C to ±500ppm/°C, make thick film power resistors excel in temperatures from -55°C to +155°C. Voltage ratings reach 2.5kV, and their low thermal resistance optimizes performance when paired with aluminum-housed designs for enhanced cooling.
Unmatched Advantages of Thick Film Power Resistors
What sets thick film power resistors apart from alternatives like wirewound or carbon composition types?
Their advantages are rooted in superior engineering:
- Compact Yet Powerful: A quarter the size of equivalent wirewound resistors, they save space while delivering high power dissipation—up to 2kW with proper heatsinking.
- Low Cost and High Yield: Simple screen-printing processes reduce manufacturing expenses, making them economical for mass production without sacrificing quality.
- Exceptional Thermal and Environmental Stability: They thrive in high-humidity, high-temperature settings, with robust coatings like polyimide and silicone gel for added protection.
- Non-Inductive and Low Noise: Ideal for precision applications, offering better pulse handling and minimal electromagnetic interference.
- High Reliability and Precision: Withstanding surges and providing stable performance over time, they outperform thin-film options in reliability for power management.
These benefits translate to longer system uptime and reduced maintenance, especially in vibration-prone environments like automotive or industrial machinery.
Primary Applications: Leveraging Thick Film Power Resistors in the Power Sector
In the electricity domain, thick film power resistors shine through their specialized roles in ensuring safe, efficient energy flow. Here are the main uses, tailored for high-stakes power electronics:
1. Grading Resistors (Voltage Dividers)
Thick film power resistors are crucial for voltage grading in high-voltage circuits, such as transformers and transmission lines. By evenly distributing voltage across multiple resistors, they prevent insulation breakdowns and hotspots. With resistance ranges up to 100MΩ and high isolation up to 12kVrms, these components maintain precise ratios in cascaded setups, like voltage-controlled oscillators or smart grid systems. In power distribution, they ensure balanced loads, reducing wear on capacitors and enhancing overall grid stability.
2. Discharge Resistors
Safety is non-negotiable in power systems, and thick film power resistors excel as discharge resistors for rapidly bleeding off stored energy in capacitors. Post-operation in UPS units or HV power supplies, they safely dissipate residual charge, preventing shocks or arcs. Their low inductance (<40nH) and surge-handling capability make them perfect for dynamic braking in motor drives or medical equipment like MRI scanners, where quick, reliable discharge is vital.
3. Filter Resistors
Noise suppression is key in power electronics, and thick film power resistors serve as filter resistors in EMI/RFI mitigation circuits. Integrated into power supply filters or inverters, they smooth out voltage ripples and harmonics, ensuring clean DC output. High power ratings (up to 2000W) allow them to handle industrial loads without overheating, while their non-inductive nature preserves signal integrity in high-frequency PWM applications.
4. Energy Absorption Resistors (Snubbers)
For surge protection, thick film power resistors act as energy absorption resistors, clamping transients in snubber networks across switches or relays. In renewable energy inverters or EV chargers, they absorb inductive kickback, safeguarding semiconductors from damage. With partial discharge specs under 10pc at 8kVrms, they provide reliable overvoltage protection, extending the life of power converters in harsh conditions.
Beyond these core uses, thick film power resistors find homes in automotive ECUs, industrial motor controls, and telecom power amps, where their compact design and thermal efficiency drive innovation.
Why Choose Thick Film Power Resistors for Your Next Project?
In summary, the thick film power resistor is more than a component—it’s a strategic enabler for resilient power systems. From voltage grading to energy absorption, its versatility addresses the challenges of modern electrification. With cutting-edge specs and proven advantages, investing in these resistors means lower costs, higher reliability, and seamless integration. Explore our range today and power your innovations with confidence. For custom solutions, contact our experts to optimize your design.