Understanding the Basics of Rod and Tube Resistors
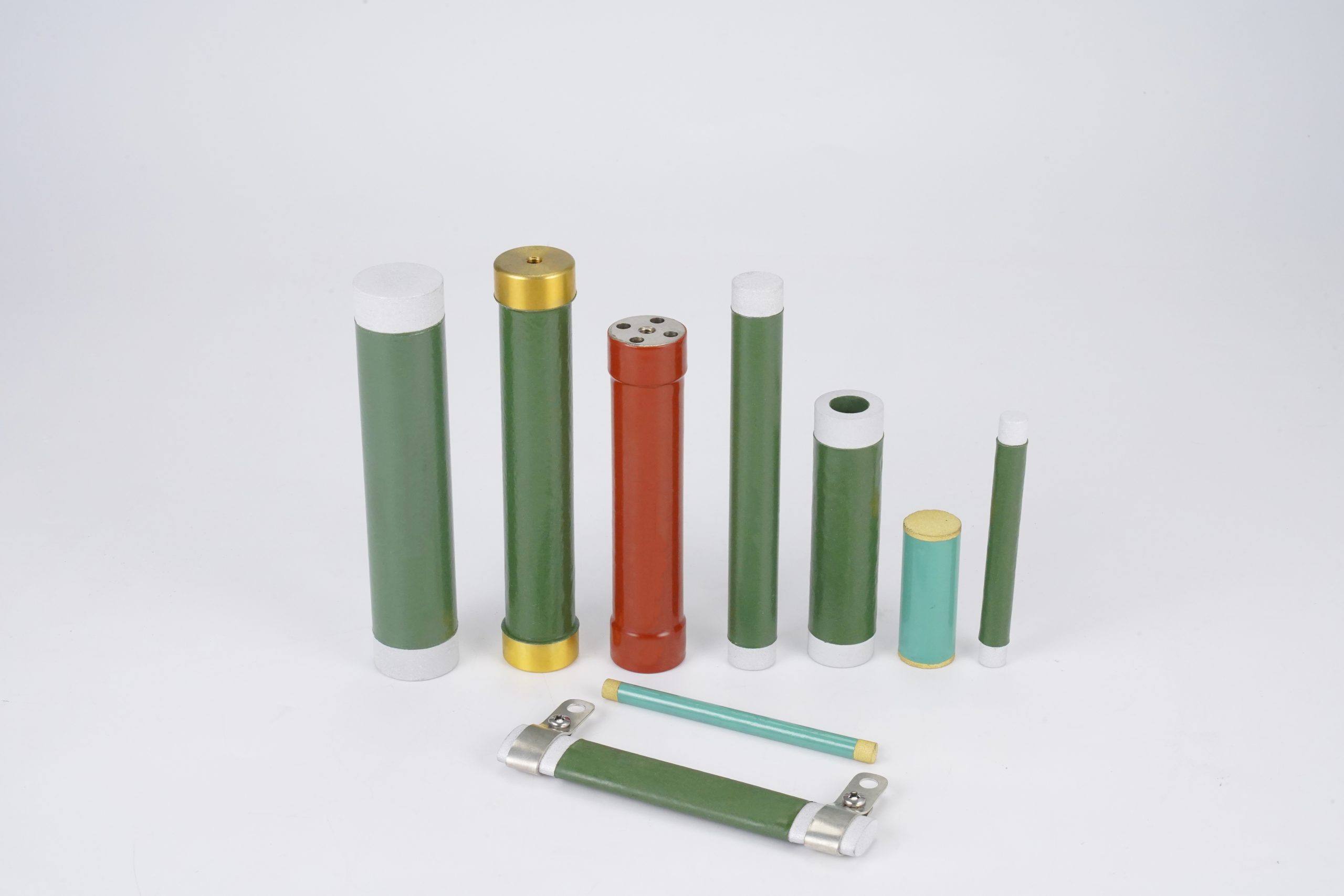
In the realm of electronic engineering, we recognize that Rod and Tube Resistors serve as integral components for various circuit applications. Their distinctive architecture allows for high thermal conductivity and effective dissipation of heat, which is imperative when operating at elevated power levels. Typically constructed from a combination of resistive materials encased within a tube or rod framework, these resistors excel in providing reliable performance across diverse frequencies.
The operational dynamics of Rod and Tube Resistors enable them to manage voltage drops while minimizing thermal expansion issues. As we explore their functionalities, it is essential to note that these resistors exhibit exceptional stability under varying temperatures, making them suitable for high-precision applications.
To illustrate their effectiveness, we can refer to the following table showcasing key specifications:
“Effective thermal management is crucial in circuit design; ensure that your resistor choice aligns with both performance specifications and environmental conditions.”
This form of resistor plays a vital role not only in achieving desired resistance values but also in enhancing overall circuit efficiency by mitigating parasitic effects that can hinder performance. In our experience, incorporating Rod and Tube Resistors into our designs has consistently yielded improvements in both stability and durability under various operational stresses. Such enhancements are indispensable when striving for optimal electronic performance in demanding applications.

The Role of Ceramic Carbon Resistors in Enhancing Circuit Performance
In our exploration of the intricate dynamics of circuit design, we recognize the pivotal role ceramic carbon resistors play in augmenting overall performance. These resistors are noted for their superior thermal stability and extended lifespan, attributes that lend themselves to enhanced reliability in high-stress environments. As we delve deeper into high-frequency applications, it becomes evident that ceramic carbon resistors exhibit lower noise levels compared to their metal film counterparts, thereby facilitating cleaner signal propagation. The precise formulation of the ceramic materials allows for minimal parasitic capacitance and inductance, characteristics essential for preventing signal distortion and maintaining circuit integrity at elevated frequencies. Furthermore, their compatibility with a range of circuit topologies renders them versatile components within a myriad of electronic frameworks. By effectively dissipating heat generated during operation, they not only contribute to circuit stability but also play a crucial role in preserving other sensitive components from thermal stress. Consequently, as designers and engineers striving for excellence in our electronic applications, it is imperative that we consider ceramic carbon resistors as essential elements that not only simplify design challenges but also promote enhanced performance metrics across various classifications of circuits.

Strategies for Managing Parasitic Effects in High-Power Applications
In the pursuit of optimizing the performance of high-power electronic circuits, we must adopt an array of strategic approaches to effectively manage parasitic effects that often hinder overall efficiency and stability. Parasitic elements, such as stray capacitance and inductance, emerge inevitably when circuit designs are pushed to operate at elevated frequencies and power levels. Therefore, we advocate for the incorporation of Rod and Tube Resistors, which possess inherent properties that facilitate enhanced performance in these challenging environments. The low inductance characteristics of these resistors significantly mitigate the adverse impacts of unwanted electromagnetic interference, thus contributing to greater signal integrity. Furthermore, precise placement and layout in conjunction with these resistors can help minimize parasitic capacitance; careful attention to trace lengths and routing can curtail the effects that negatively influence circuit behavior. Additionally, our implementation of proper shielding techniques alongside Rod and Tube Resistors allows us to create a more robust circuit design, safeguarding against external noise sources that may further amplify parasitic effects. Utilization of simulation tools also plays a critical role in our methodology; by modeling circuits with integrated parasitics, we can anticipate challenges and refine designs before fabrication, ensuring that we are prepared to optimize performance from initial concept through final deployment. Through these multifaceted strategies centered around Rod and Tube Resistors, we not only enhance our circuits’ resilience but also pave the way for advancements in high-power applications that demand uncompromised stability and efficiency.
Comparing Ceramic Carbon Resistors to Other Resistor Types in Electronics
When we delve into the intricacies of resistor types, specifically the comparison between ceramic carbon resistors and alternative designs, we unearth a myriad of parameters that dictate their suitable applications in electronic circuits. Ceramic carbon resistors are distinguished by their exceptional stability under varying temperature conditions, which enables them to maintain consistency in performance across a range of operational thresholds. In contrast, traditional resistors may falter, particularly when subjected to fluctuations typical of high-power applications. We recognize that resistance to thermal drift is pivotal; therefore, the thermal performance of ceramic carbon types often renders them favorable in environments where precision is demanded and parasitic effects can adversely skew circuit behavior.
Moreover, the construction materials inherent in ceramic carbon resistors lend them an advantage regarding noise characteristics and inductance properties. When juxtaposed with metal film or wire-wound resistors—to name a couple—we observe that ceramic carbon designs mitigate unwanted parasitic noise more effectively due to their inherent structure and composition. This aspect is particularly crucial when addressing high-frequency applications where even minute variances can lead to significant performance degradation.
In addition, we must acknowledge the cost-efficiency argument often levied against certain high-end resistor types. Although entailing a relatively straightforward manufacturing process as compared to specialized low-noise or precision resistors, ceramic carbon resistors strike an exceptional balance between affordability and quality, making them an attractive alternative for many designers looking for viable performance within budget constraints.
This comparative examination ultimately underscores our commitment to understanding the functional paradigms defining various resistor technologies; it allows us to make informed choices that will ensure optimized circuit design tailored to specific operational environments while deliberating on both technical functionalities and economic factors essential for project feasibility.