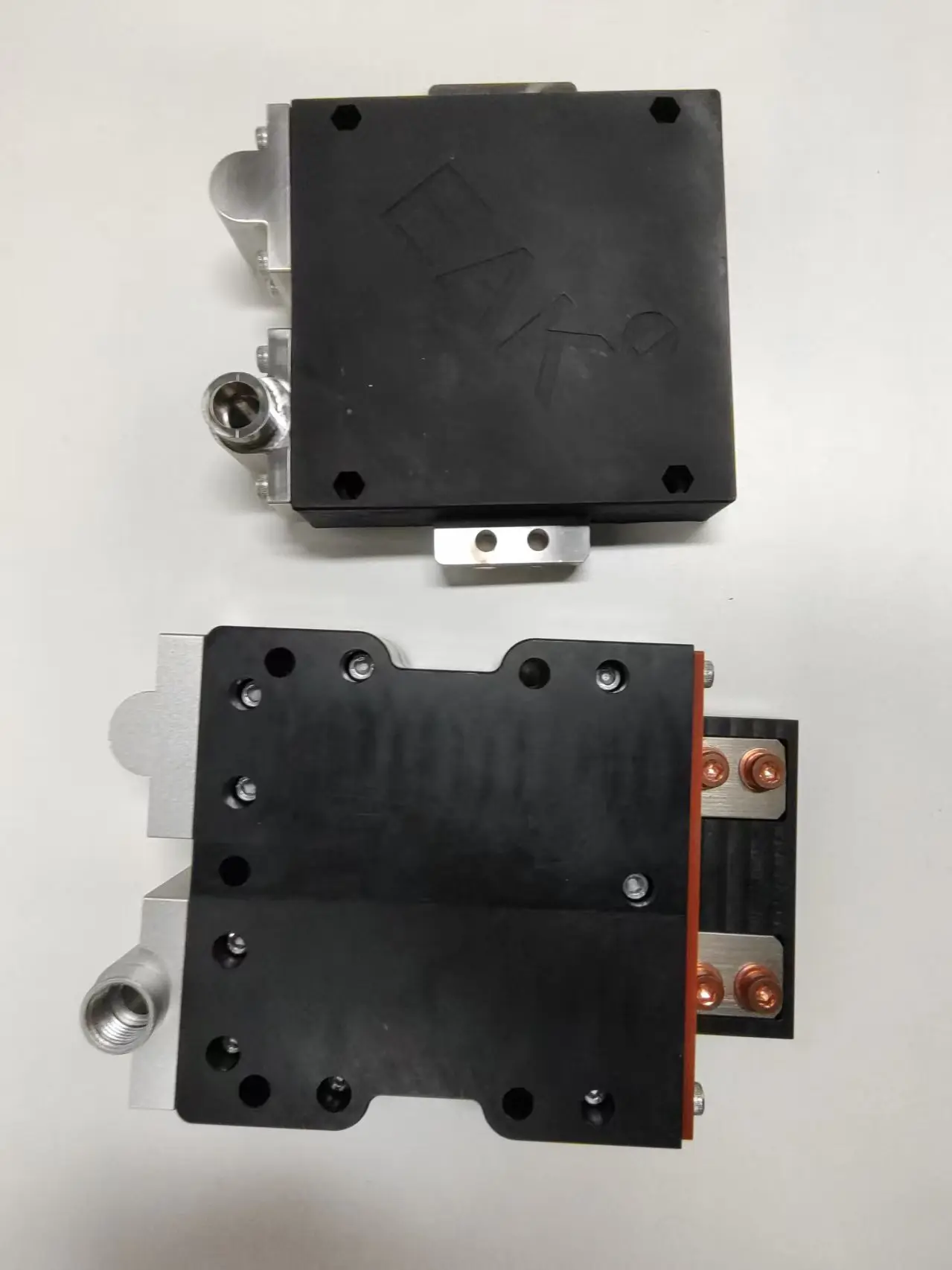
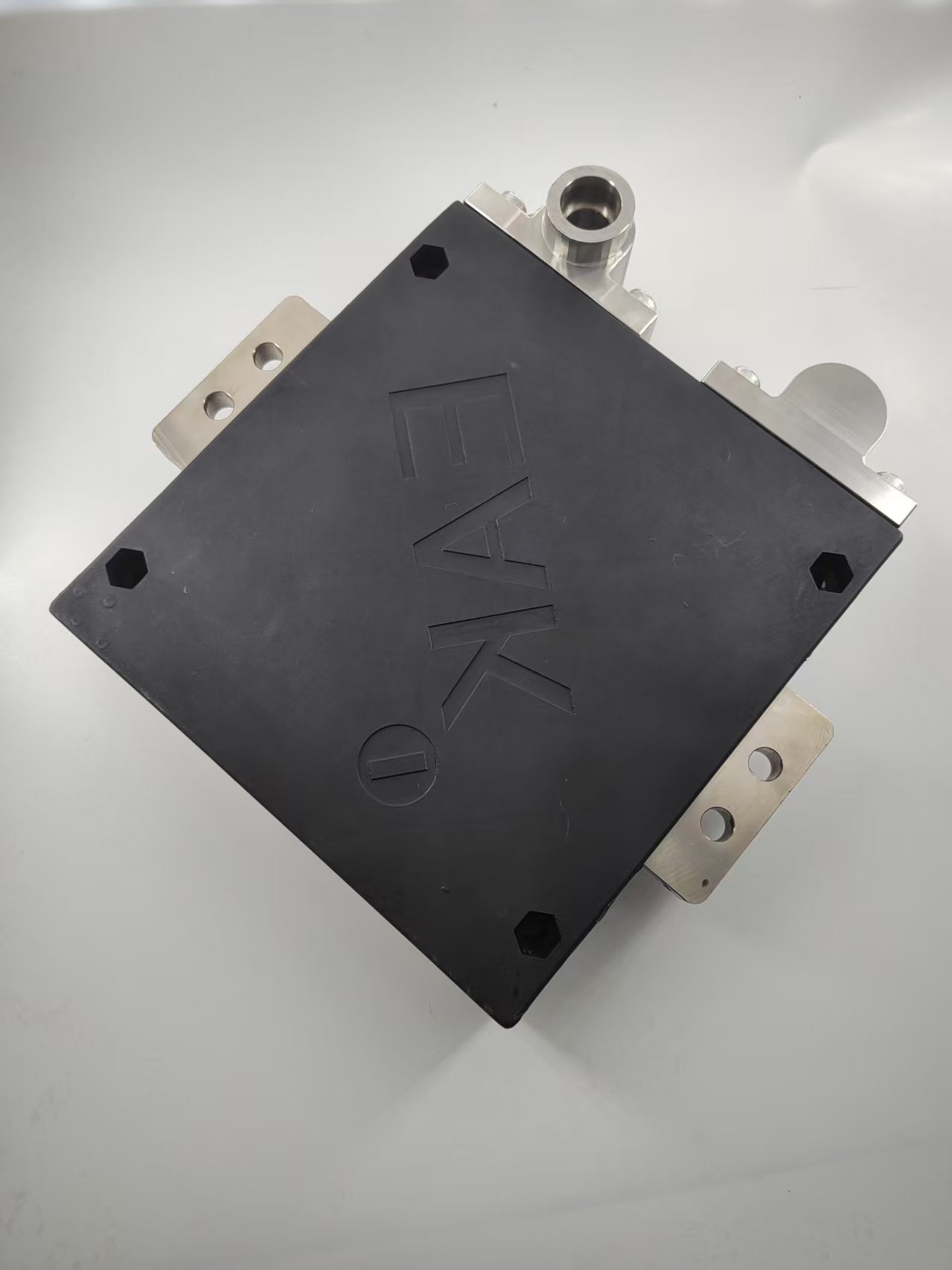
In the realm of power generation, managing high power levels and ensuring system stability are critical. One of the essential components enabling this is the liquid-cooled resistor. These specialized resistors are designed to handle significant electrical loads while efficiently dissipating heat through liquid cooling systems. This article explores what liquid-cooled resistors are, their applications in power generation, and why they are indispensable in modern electrical infrastructure.
What is a Liquid-Cooled Resistor?
A liquid-cooled resistor is a high-power resistor that uses a liquid coolant—such as water or oil—to transfer heat away from the resistor element. Unlike air-cooled resistors, liquid-cooled variants are capable of dissipating much higher amounts of heat, making them suitable for demanding industrial applications. Their construction typically involves a resistor element immersed in or connected to a cooling liquid, which circulates continuously to maintain optimal operating temperatures.
Why Are Liquid-Cooled Resistors Critical in Power Generation?
Power generation facilities, including thermal, nuclear, and renewable energy plants, require components that can withstand and operate reliably under extreme conditions. Liquid-cooled resistors meet this need due to several key advantages:
- High Heat Dissipation: They efficiently remove heat generated during high-current operations, preventing overheating and potential equipment failure.
- Handling High Power Levels: Capable of managing large electrical loads, they are suitable for use in high-voltage and high-current environments.
- Enhanced Reliability and Longevity: The effective cooling extends the lifespan of the resistor and reduces maintenance requirements.
- Stable Operation: They provide consistent performance, crucial for maintaining grid stability and safe operation of power systems.
Main Applications of Liquid-Cooled Resistors in Power Generation
Liquid-cooled resistors are integral to various critical equipment within power plants. Here are some of the primary devices and scenarios where these resistors are employed:
| Equipment | Application & Role |
|
|---|
Specific Roles of Liquid-Cooled Resistors in Power Generation Equipment
- Starting Resistances: During the startup phase of large generators, liquid-cooled resistors limit the inrush current, preventing damage and ensuring smooth startup procedures.
- Short-Circuit Current Limiting: In case of faults or short circuits, these resistors absorb excess energy, protecting vital equipment from catastrophic failure.
- Load and Voltage Regulation: They help in maintaining consistent voltage levels by controlling excitation currents and reactive power, contributing to grid stability.
Benefits of Using Liquid-Cooled Resistors in Power Plants
- Safety: Their superior heat dissipation prevents overheating, reducing fire risks and equipment damage.
- Efficiency: They enable high power handling without compromising performance, optimizing plant operations.
- Cost Savings: Longer lifespan and lower maintenance requirements lead to reduced operational costs over time.
Final Thoughts
Liquid-cooled resistors are vital components in the power generation industry. Their ability to dissipate large amounts of heat efficiently, handle high electrical loads, and provide reliable operation makes them indispensable for maintaining safe, stable, and efficient power systems. Whether used in startup procedures, fault protection, or load regulation, liquid-cooled resistors ensure the robustness and longevity of critical electrical infrastructure.
Are you interested in learning more about specific types of liquid-cooled resistors or their technical specifications? Would you like insights into how to select the right resistor for your power plant? Feel free to ask!