In the competitive landscape of advanced engineering, traditional metal components are facing increasing challenges regarding corrosion, mechanical wear, and material limitations. A revolutionary solution has emerged: Ultra-Low Resistivity Conductive Ceramics. This advanced material successfully merges the robust durability of technical ceramics with the essential electrical properties of metals, providing a game-changing alternative for high-performance applications.
Unmatched Material Specifications and Advantages
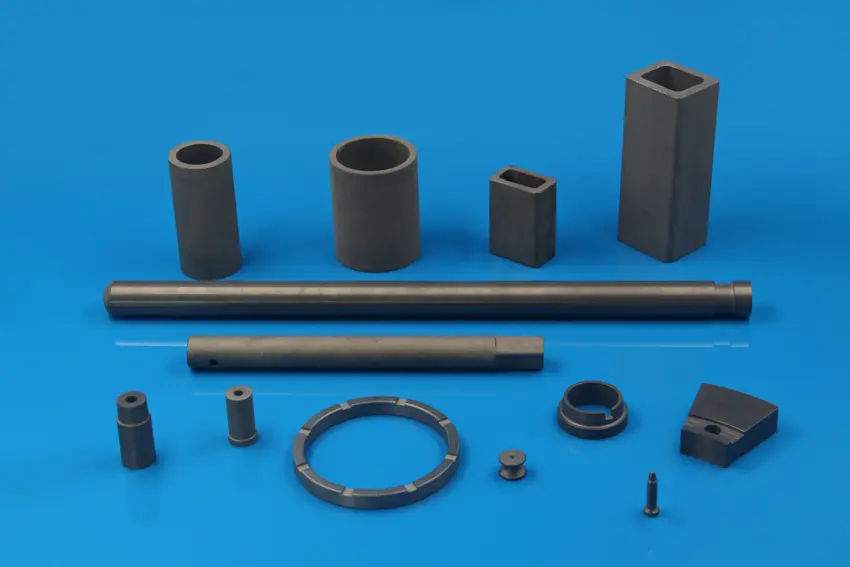
Ultra-Low Resistivity Conductive Ceramic products are precision-engineered from specialized ceramic powders using advanced forming techniques like isostatic pressing and injection molding. The resulting material offers a unique combination of technical advantages:
Exceptional Electrical Conductivity: The core technical characteristic is the remarkably low material resistivity, measured at 10−7Ω⋅m. This allows these components to function effectively as high-performance electrical conductors.
Superior Corrosion Resistance (Plating-Free): The innate chemical stability of the ceramic base eliminates the need for metal plating. This solves critical corrosion issues often seen in metal products, allowing for long-term use in harsh, corrosive environments.
Outstanding Wear Performance: These components exhibit high wear resistance, making them an excellent choice to replace materials like tungsten steel. The material boasts a high hardness value of 20.4±0.6 GPa.
High Mechanical Strength: The material maintains structural integrity with a high flexural (bending) strength of 300.6±35 MPa
Key Product Forms and High-Value Applications
The material can be processed into various shapes to meet stringent industry demands, providing both the conductivity of metal and the corrosion/wear resistance of ceramics.
| Product Form | Technical Function & Application Area |
|---|---|
| Conductive Ceramic Pins and Studs | Precision electrical contact points and charging terminals. Key applications include: |
| * Medical Devices (Medical sensors, charging PINs) | |
| * Health Devices (Smart wearable ECG devices, smart wearable/Bluetooth headset charging PINs) | |
| * Smart Transportation (Automotive sensors) | |
| Conductive Ceramic Discs and Plates | Used for large-contact surface electrical interfaces and components requiring broad surface resistance. Applications include: |
| * Medical Aesthetics Equipment | |
| * Semiconductor Devices (Corrosion-resistant, low-conductive parts) | |
| * Petrochemical Industry (Wear- and corrosion-resistant components) | |
| Conductive Ceramic Custom Shapes | Complex components like columns, pots, or other irregular geometries for specialized industrial equipment. Applications include: |
| * Metallurgy and Chemical Industry (Crucibles for rare metal smelting) | |
| * Smart Equipment (Conductive, wear-resistant, and corrosion-resistant parts) |
By leveraging these unique characteristics, ultra-low resistivity conductive ceramics are becoming the material of choice for engineers seeking to push the boundaries of miniaturization, durability, and reliability across demanding applications.