In the modern era of electrification, driven by the pursuit of higher performance, longer range, and smarter control, vehicles and industrial equipment must safely and efficiently manage the immense energy generated during braking. Traditional air-cooled braking systems are no longer sufficient when faced with the challenges of high power and high cycling. At this juncture, the integrated solution of a high-power brake chopper and a liquid-cooled resistor has emerged. This is not merely a combination of components, but a precision device that fuses power electronics, thermodynamics, and systems engineering into one, specifically designed for the most demanding applications.
What is an Integrated Liquid-Cooled Brake Chopper?
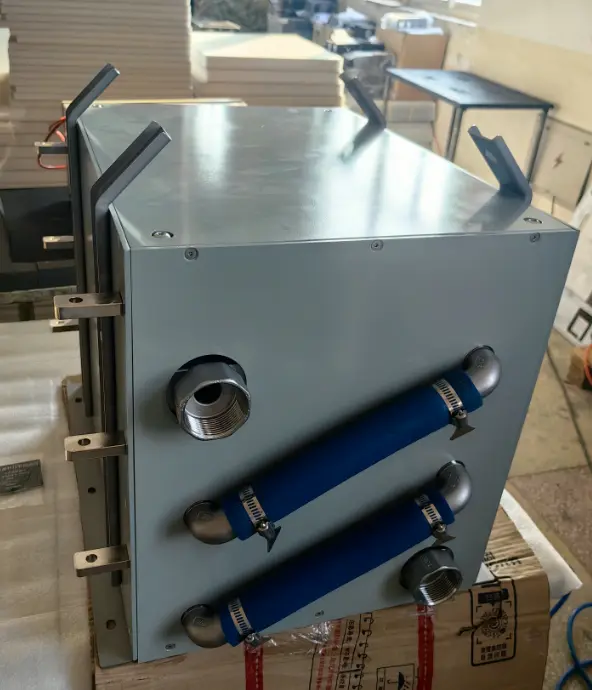
Simply put, it is a single module that encapsulates a high-voltage DC (HV DC) chopper (a high-speed electronic switch) and a high-power liquid-cooled brake resistor within a single, robust enclosure. When a vehicle’s regenerative braking system cannot absorb all the energy, this integrated unit activates immediately, directing the excess electrical energy to the internal resistor, which then converts it into heat and efficiently dissipates it via a circulating coolant.
Why are “Integration” and “Liquid Cooling” the Inevitable Choice for High-Power Applications?
For applications requiring the handling of hundreds of kilowatts, such as large electric buses, mining trucks, rail transit, or port cranes, the integrated liquid-cooled design offers unparalleled advantages:
- Unmatched Heat Dissipation Performance This is the core advantage of the integrated liquid-cooled solution. The specific heat capacity of liquid is far greater than that of air, enabling it to remove heat with extremely high efficiency. According to technical specifications, such systems can typically operate continuously and stably at coolant temperatures as high as 75°C. The highly efficient liquid cooling circuit ensures that the IGBTs (Insulated Gate Bipolar Transistors) and the resistor remain within safe temperature limits under high loads, preventing performance degradation or system shutdown due to overheating, thereby achieving sustained high power density.
- Ultimate Compactness and Lightweight Design Integrating two key components into one eliminates the need for separate mounting brackets, complex high-voltage cabling, and additional coolant lines. This highly integrated design significantly reduces the overall volume and weight. For mobile applications where space and weight are extremely precious, this means more space can be freed up for batteries or other equipment, and the vehicle’s weight distribution can be optimized, enhancing overall efficiency.
- Exceptional System Reliability Reducing external connection points is equivalent to reducing potential failure sources. The integrated design means fewer cable connectors and fewer coolant line interfaces, thereby lowering the risk of leaks or failures caused by vibration, dust, moisture, or loose connections. Products typically feature an IP67 protection rating, providing complete protection against dust and resistance to powerful water jets, ensuring long-term, reliable operation in harsh industrial environments that are dusty, humid, and subject to high vibration.
- Millisecond-Level Fast Response and Multi-Layer Protection High-power applications have extremely high demands for safety. Integrated choppers often feature an autonomous control mode that can monitor the bus voltage directly with an ultra-fast response time of <1ms. When the voltage exceeds a preset threshold, the system can activate within an extremely short time to protect the battery and motor controller. Simultaneously, built-in multi-layer protection mechanisms, such as overvoltage, overcurrent, overtemperature, and the unique low-resistance/peak current too high (RLow) detection, can effectively prevent catastrophic consequences caused by external resistor faults, ensuring the system is fail-safe.
- Intelligent CAN Bus Communication and Flexible Control Modern integrated choppers are intelligent “networked” devices. They are based on standard CAN bus protocols like SAE J1939, enabling seamless communication with the vehicle’s main controller. Users can set power, voltage thresholds, or duty cycles in real-time via the bus and receive critical data such as system operating status, temperature, and current. Even if CAN bus communication fails, its autonomous mode can act as a safety redundancy, guaranteeing continuous system protection.
How to Select the Right Integrated Liquid-Cooled Chopper?
When selecting, you need to clearly define the following key parameters:
- Maximum Bus Voltage (VInMax) and Maximum Input Current (IInMax): This determines the system’s power handling capability.
- Maximum Coolant Temperature (TCoolMax) and Minimum Coolant Flow (QMin): Ensure your cooling system can meet the requirements.
- Control Method: Do you need autonomous control, or precise external control via a CAN bus?
- Mechanical Type: Choose between an integrated type (Type D) or a separate type based on your system design.
Conclusion
The integration of a high-power brake chopper with a liquid-cooled resistor represents a significant leap forward in energy management technology. It is not just a component, but a system-level solution optimized for reliability, efficiency, and compactness. As electrification continues to advance, this module, which integrates efficient heat dissipation, intelligent control, and ultimate reliability, is becoming the “unsung hero” ensuring the safe and efficient operation of heavy-duty electric vehicles and industrial equipment. Choosing an integrated liquid-cooled solution is choosing a stronger, more secure future for your high-power application.