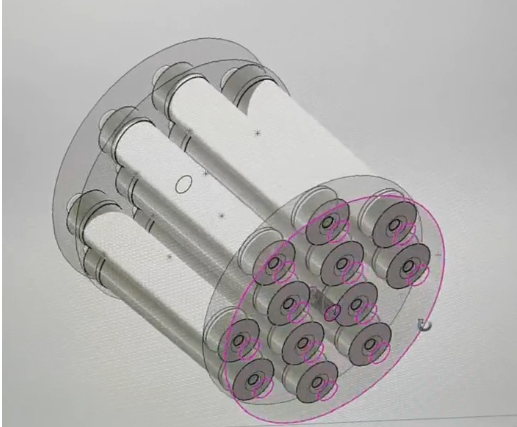
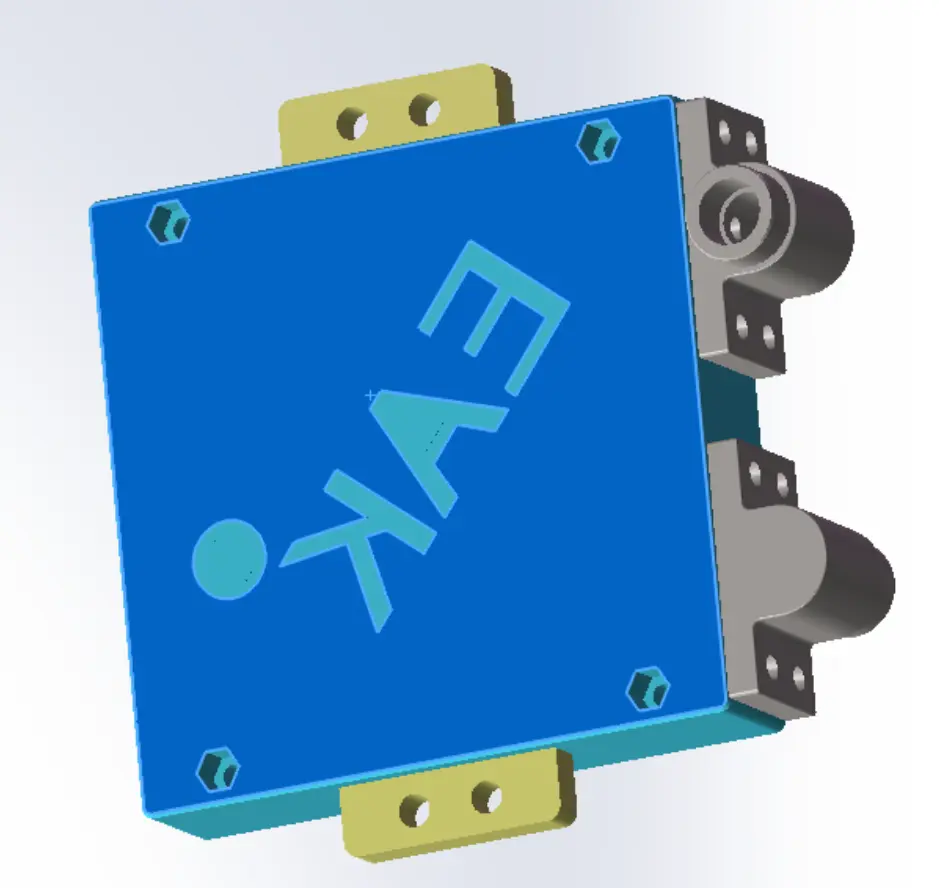
In the rapidly evolving landscape of power electronics, liquid-cooled resistors have emerged as a critical component in optimizing the performance of Insulated Gate Bipolar Transistors (IGBTs). These resistors play a pivotal role in shaping waveforms, filtering unwanted noise, and enhancing the overall efficiency of IGBT-based systems. This article delves into the advantages of liquid-cooled resistors, their applications in IGBT circuits, and how they contribute to superior system performance.
The Role of IGBTs in Power Electronics
IGBTs are widely used in high-power applications such as motor drives, renewable energy inverters, electric vehicles, and industrial automation. They combine the high input impedance of MOSFETs with the low on-state resistance of bipolar transistors, making them ideal for switching high currents at high voltages. However, IGBTs are sensitive to voltage spikes, current oscillations, and electromagnetic interference (EMI), which can degrade their performance or even cause failure.
To address these challenges, engineers often incorporate external components like liquid-cooled resistors into the circuit design. These resistors not only protect the IGBT but also enhance its switching characteristics by providing waveform shaping and filtering capabilities.
Why Choose Liquid-Cooled Resistors?
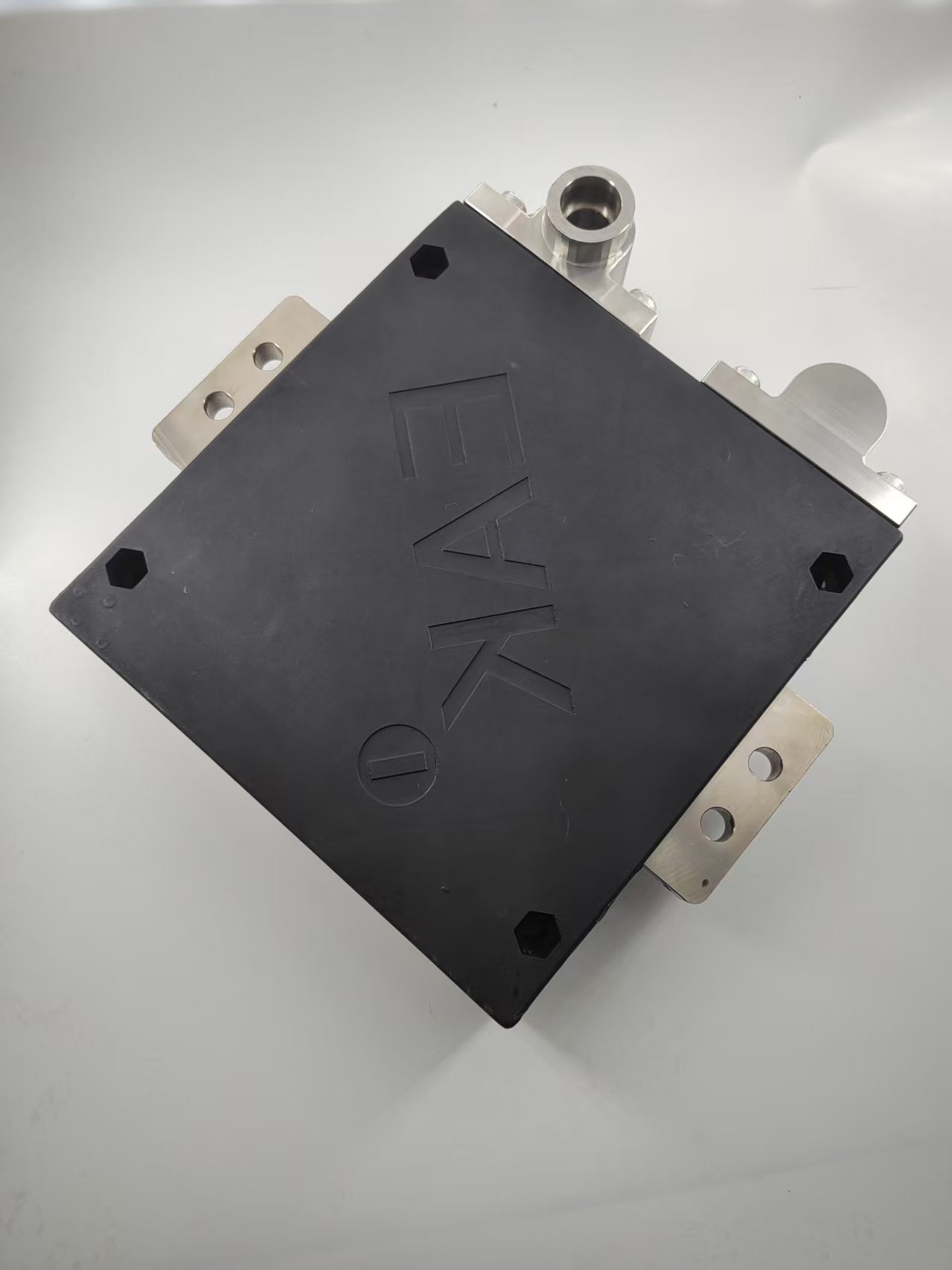
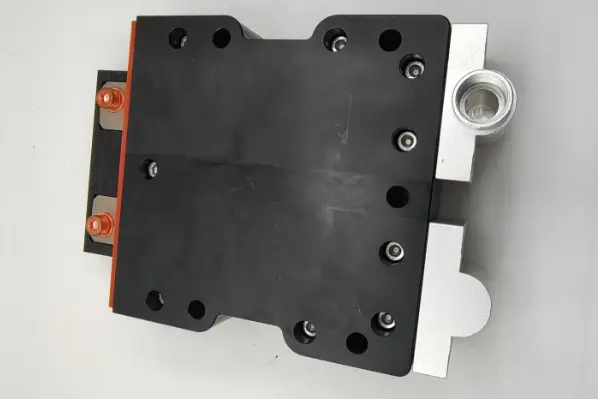 Liquid-Cooled Resistors
Liquid-Cooled Resistors
Liquid-cooled resistors are specifically designed to handle high power densities while maintaining optimal thermal performance. Unlike air-cooled resistors, which rely on convection to dissipate heat, liquid-cooled resistors use a closed-loop cooling system that transfers heat away from the resistor element efficiently. This makes them ideal for demanding applications where space is limited, and thermal management is critical.
Here are some key advantages of liquid-cooled resistors:
- High Power Handling Capacity : Liquid-cooled resistors can absorb and dissipate large amounts of energy, making them suitable for high-power IGBT applications.
- Compact Design : Their efficient cooling mechanism allows for a smaller footprint compared to traditional resistors.
- Reduced Thermal Stress : By maintaining stable operating temperatures, liquid-cooled resistors extend the lifespan of IGBTs and other components in the circuit.
- Low Noise Operation : The robust design minimizes vibrations and acoustic noise, ensuring quiet operation even under heavy loads.
Applications of Liquid-Cooled Resistors in IGBT Systems
1. Waveform Shaping
IGBTs require precise control over their switching behavior to minimize losses and improve efficiency. During turn-on and turn-off transitions, voltage spikes and current oscillations can occur due to parasitic inductance and capacitance in the circuit. Liquid-cooled resistors are used in snubber circuits to dampen these oscillations and shape the voltage and current waveforms.
For example, an RC snubber circuit incorporating a liquid-cooled resistor can effectively suppress voltage spikes during IGBT turn-off. This ensures smooth switching transitions, reduces EMI, and prevents damage to the IGBT.
2. Energy Dissipation
In dynamic braking applications, IGBTs often need to dissipate excess energy generated during deceleration. A liquid-cooled resistor acts as a dynamic braking resistor, safely converting this energy into heat without overheating. This application is common in electric vehicles and industrial motor drives.
3. Filtering Unwanted Noise
High-frequency noise generated during IGBT switching can interfere with other electronic components in the system. By integrating a liquid-cooled resistor into a low-pass filter circuit, engineers can attenuate high-frequency harmonics and ensure clean power delivery.
4. Soft Start and Load Testing
During system startup, sudden inrush currents can stress the IGBT and surrounding components. A liquid-cooled resistor can be used as a soft-start resistor to gradually increase the load, protecting the IGBT from excessive current surges. Additionally, these resistors are invaluable for load testing IGBTs under various operating conditions, ensuring reliable performance before deployment.
Conclusion
The integration of liquid-cooled resistors into IGBT-based systems offers unparalleled benefits in terms of waveform shaping, filtering, and energy management. Their ability to handle high power densities while maintaining excellent thermal performance makes them indispensable in modern power electronics. Whether you’re designing motor drives, renewable energy systems, or electric vehicles, leveraging the capabilities of liquid-cooled resistors will undoubtedly elevate your system’s reliability and efficiency.